Topic
Agri-food systems enabled by interconnected digital technologies that are more transparent to consumers, farmers and other stakeholders along the agri-food value chain.
Introduction
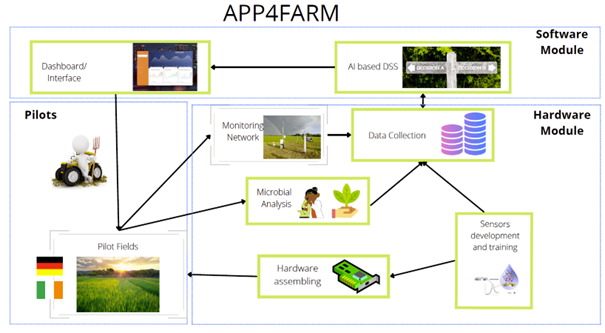
The objective of APP4FARM is the definition of an ICT infrastructure allowing the farmer to monitor nitrogen loss, allowing efficient management of nitrogen-based fertilisers. This will ensure control of farming costs and nitrogen oxide emissions in the atmosphere leading to the improvement of both GHG levels (N2O) and local air quality (nitrogen oxides, secondary inorganic aerosol, and ozone). The infrastructure will include a monitoring system allowing to trace all the meteorological data and nitrogen emission levels, driving a Decision Support System that will give the farmer all the measured data and the forecasts up to 3 days in advance. The presented solution will grant all the data needed to ensure to the consumer the full traceability of the production conditions and the transparency on the environmental impact, supporting the decision makers to define the “green tag” along the whole supply chain.
Background
Nitrogen is the primary nutrient critical for the productivity of agricultural ecosystems. Nevertheless, large changes in the availability of nitrogen can lead to severe alterations in the nitrogen cycle in terrestrial ecosystems. The EU Nitrogen Expert Panel, in 2015, proposed an easy-to-use indicator for ‘nitrogen use efficiency’ (NUE), applicable to agricultural land, farms, and whole food production–consumption systems (EU Nitrogen Expert Panel, 2015). Currently, NUE estimates the N surplus as the difference between input and output. To understand the losses, the emission related to single farming systems and climatic zones need to be accurately measured and integrated into a Decision Support System (DSS) in order to design better N management strategies aiming at achieving agronomic objectives (farm income, high crop, and animal productivity) and environmental objectives (minimal N losses), simultaneously.
Main project activities
- Definition of Decision Support System (DSS) to support the optimal use of nitrogen-based fertilizers:
- Development of the dashboarding system for the DSS
- Development of Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence forecasting models
- Definition of the sensing system to monitor environment and soil health
- Design tailored sensors for N-related microbial activity in soil
- Definition of a virtual sensor linking environmental variables and N-related microbial diversity in soil
Expected social impact
- Possibility to access the monitored data to make it publicly available, ensuring the transparency of the supply chain from the very beginning.
- Possibility to use the data to start a “green labeling” project.
- Availability on the market of more traced, sustainable, and healthy food.
- Limitation of the GHG (N2O) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions.
- Limitation of the concentration in the atmosphere of ozone (O3) and aerosol (PM10/PM2.5).
- Data transparency
Keywords
- Decision Support System Satellite Controlled incentive
- Nitrogen oxides
- Fertilisers
- Tailor made MOX sensors
Project coordinator
Prof. Carnevale - University of Brescia, UNIBS, Italy
Partners
- ITALY: Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, CNR-IBBR
- GERMANY: German Research Centre for Geosciences, GFZ
- ITALY: University of Florence, UNIFI
- IRELAND: Munster Technological University, MTU
Expected project start date and end date
The APP4FARM project starts on April 2023 and runs until March 2026.
Topic
Agri-food systems enabled by interconnected digital technologies that are more transparent to consumers, farmers and other stakeholders along the agri-food value chain.
Introduction
The objective of APP4FARM is the definition of an ICT infrastructure allowing the farmer to monitor nitrogen loss, allowing efficient management of nitrogen-based fertilisers. This will ensure control of farming costs and nitrogen oxide emissions in the atmosphere leading to the improvement of both GHG levels (N2O) and local air quality (nitrogen oxides, secondary inorganic aerosol, and ozone). The infrastructure will include a monitoring system allowing to trace all the meteorological data and nitrogen emission levels, driving a Decision Support System that will give the farmer all the measured data and the forecasts up to 3 days in advance. The presented solution will grant all the data needed to ensure to the consumer the full traceability of the production conditions and the transparency on the environmental impact, supporting the decision makers to define the “green tag” along the whole supply chain.
Background
Nitrogen is the primary nutrient critical for the productivity of agricultural ecosystems. Nevertheless, large changes in the availability of nitrogen can lead to severe alterations in the nitrogen cycle in terrestrial ecosystems. The EU Nitrogen Expert Panel, in 2015, proposed an easy-to-use indicator for ‘nitrogen use efficiency’ (NUE), applicable to agricultural land, farms, and whole food production–consumption systems (EU Nitrogen Expert Panel, 2015). Currently, NUE estimates the N surplus as the difference between input and output. To understand the losses, the emission related to single farming systems and climatic zones need to be accurately measured and integrated into a Decision Support System (DSS) in order to design better N management strategies aiming at achieving agronomic objectives (farm income, high crop, and animal productivity) and environmental objectives (minimal N losses), simultaneously.
Main project activities
Expected social impact
Keywords
Project coordinator
Prof. Carnevale - University of Brescia, UNIBS, Italy
Partners
Expected project start date and end date
The APP4FARM project starts on April 2023 and runs until March 2026.